4 Fun Facts About Two-Way Radios
Two-way Radio
Although two-way radios (also known as walkie-talkies) are not used frequently in our daily lives, they are indispensable in various industries and workplaces where instant communication is essential, today let's talk about few things about two-way radio.
What's a two-way radio?
Compared to an old-fashioned broadcasting radio that only receives radio programs, a two-way radio is a device that can both receive and transmit radio signals to realize communication purposes. A high-powered, large-sized, and fixedly installed in a certain place (car, ship) is called a radio station. A low-powered, small-sized, and portable walkie-talkie is called a handheld two-way radio, which is also what we commonly refer to as a walkie-talkie.
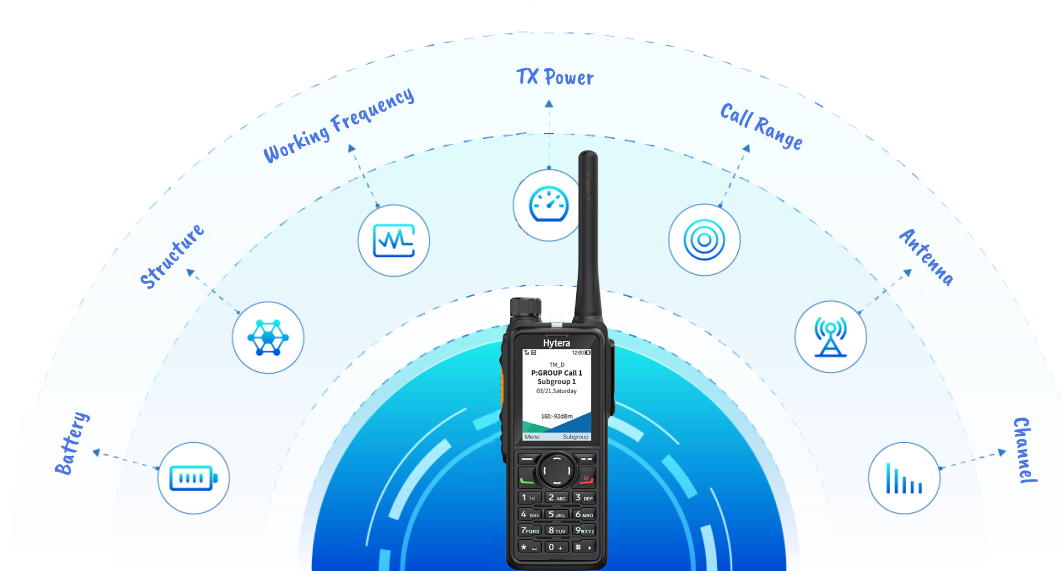
The Features of a Two-Way Radio
Compared with mobile phones, walkie-talkies have very obvious characteristics: most two-way radios (walkie-talkies) that have established a call channel can talk to one another directly without relying on a cell network by just pressing the call button. If multiple walkie-talkies are on the same channel, when one walkie-talkie starts talking, all other walkie-talkies can receive the sound. No call or traffic charges are generated. walkie-talkies convert the sound made by people into invisible radio waves. and the communications are made free of charge. If you need to talk to an individual or a group frequently, walkie-talkies can save a lot of call costs. PS: Radio calls are free, but you still need to pay a license fee for occupying the channel.
The History of Two-Way Radios
1. Analog Two-Way Radio
Since its invention, Two-way radios have undergone many changes. The earliest type of walkie-talkie uses analog signals, mainly modulating the signal to the communication frequency band of the walkie-talkie. Two walkie-talkies need to use the same communication channel within the call range to successfully communicate.
2. Digital Two-Way Radio
Digital technology is then introduced to allow multiple users to use the same frequency band at the same time, thereby increasing the communication capacity and frequency resource utilization efficiency. A digital two-way radio uses digital signals to convert voice into digital codes and transmit them between different walkie-talkies, which can effectively avoid noise, distortion and other problems during the call.
3. Broadband Two-Way Radio (Public Network Walkie-talkies)
With the emerging of video, positioning, and more cellphone applications and the evolving of public network communication standards, broadband two-way radios came into being. They add the cell network coverage to the existing communication network to achieve the expansion of the call coverage. This type of walkie-talkie, like a PoC radio, however, needs a SIM card, so their maximum call distance can exceed 5,000 kilometers. They are more like cell phones with two-way radio featuring capabilities, such as push-to-talk, real-time one to many call, etc.
How Does Two-way radio work?
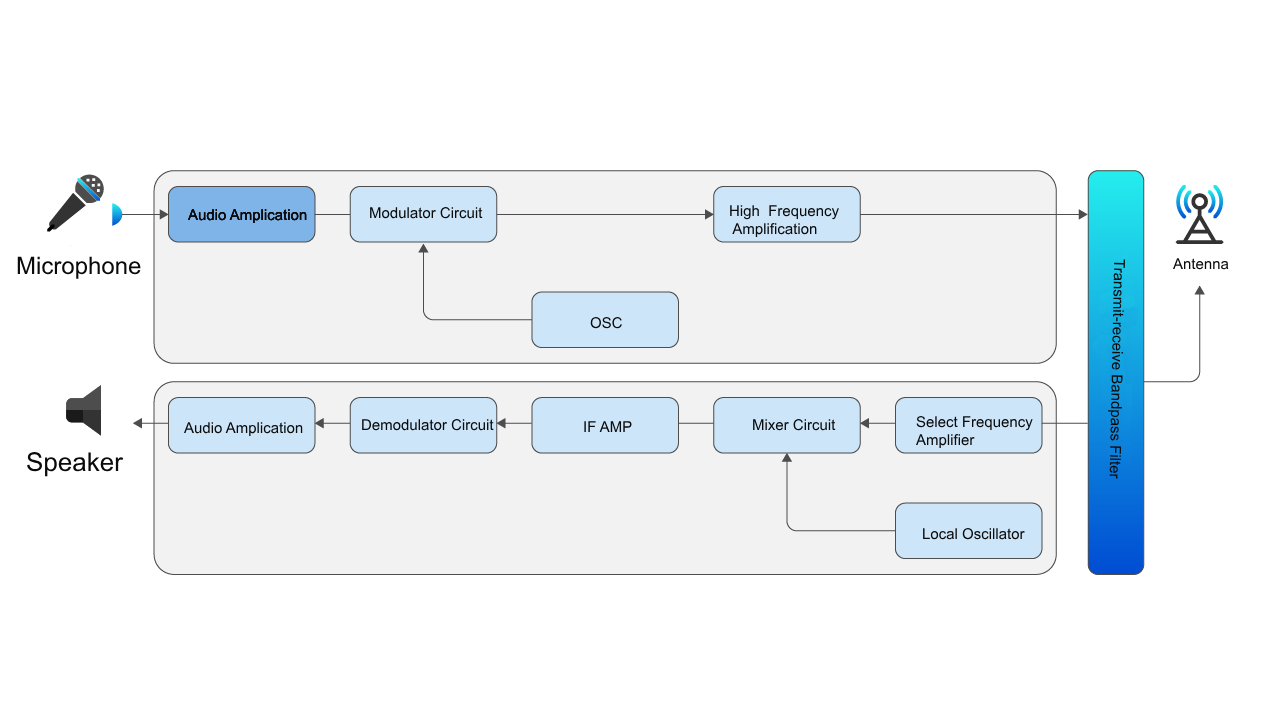
The process of a typical walkie-talkie initiating a call: receiving input (can be voice or text) ---> processing information (encoding the input into a signal) ---> sending a signal (sending it to another walkie-talkie or sending it to an application server through the operator network).
The process of a walkie-talkie answering a call: receiving a signal (from another walkie-talkie or application server) ---> processing information (decoding the signal into voice or multimedia) ---> output.
These fascinating facts highlight the enduring significance of two-way radios as versatile tools for communication, collaboration, and safety in various contexts, both historic and contemporary. If you have any technology question or solution request about Hytera two-way radio, contact us now!





