What is an Analog and Digital Radio?
Two-way Radio
Analog and digital radios represent two distinct approaches to transmitting information, each with its unique advantages and drawbacks.

Analog Signals: Simplicity and Familiarity
Analog technology, known for its continuous wave transmission, offers smooth handling of signal changes and maintains some intelligibility even in the presence of interference. However, it's more susceptible to noise and less efficient in its spectrum usage.
Digital Signals: Clarity and Advanced Features
Digital technology utilizes binary data packets (1s and 0s), providing superior audio quality and resistance to interference. While digital signals either transmit perfectly or not at all, this reliability ensures clear communication even in challenging conditions.
Hybrid Radios: Bridging the Gap
Hybrid radios, like Hytera's HP50X and HP56X, offer the best of both worlds, providing a seamless transition for organizations with existing analog infrastructure seeking the benefits of digital technology.
These innovative solutions combine the advanced security of digital technology with full compatibility with analog systems, giving you the best of both worlds.
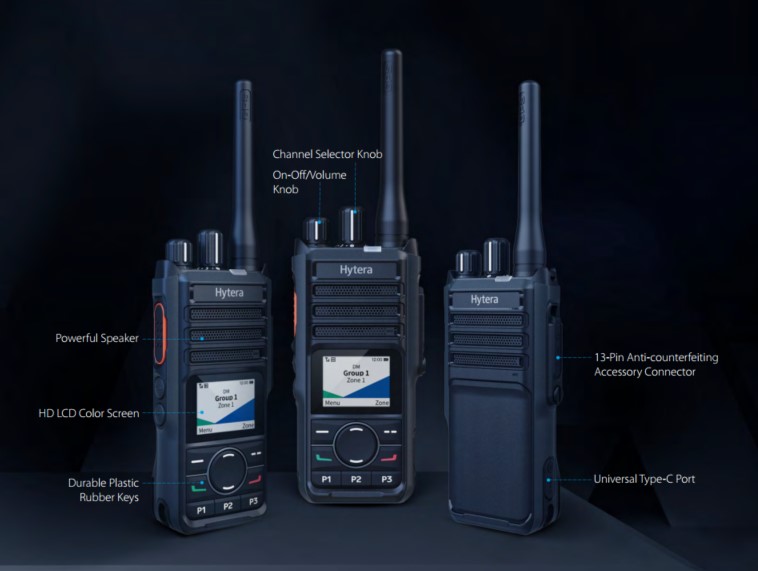

Analog and Digital Signals: Differences
Analog signal characteristics
One of the main advantages of analog technology is its ability to handle signal changes smoothly and continuously. This means that even when there is interference, the signal is still understandable, albeit noisy. It is a system that degrades progressively rather than abruptly dropping out, which can be crucial in critical situations.
However, analogue technology also has its limitations. For example, it is more susceptible to noise and interference. In urban environments or in places with many obstructions, signal quality can decrease significantly. In addition, spectrum use in analogue technology is not as efficient as in digital technology, which means there can be problems with congestion on busy channels.
Characteristics of digital signal
In contrast, a digital signal is represented as a series of pulses or “packets” of binary data. Each pulse represents a specific state (0 or 1), making the signal much less susceptible to interference. While an analog signal can progressively lose quality, a digital signal is either transmitted correctly or not transmitted at all. This means that with digital radio, it is possible to maintain higher communication quality, even in poor signal conditions.
For more on the differences between analog and digital radio, we have another blog post.
Digital Network and Analog Network
Operation and characteristics of an analog network
In the context of a communications network, especially in professional applications such as in security forces, emergency services or large industries, the choice between a digital network and an analogue network can be crucial.
An analog network is simple and effective, ideal for voice communications where constant connectivity and operational simplicity are the priority. These networks have been used for years and are known for their reliability. However, they are not as flexible or as secure as digital networks. Security on an analog network can be an issue, as transmissions can be intercepted relatively easily, and data cannot be sent efficiently.
Operation and characteristics of a digital network
Digital networks, on the other hand, offer a number of advantages that make them increasingly popular in the professional field. For example, a digital network allows not only voice transmission with superior quality, but also the transmission of data, which opens up a multitude of possibilities for advanced applications, such as fleet management, location tracking, and secure communications through encryption.
Example of integration of both technologies: hybrid networks
An interesting example of the combination of both technologies is the use of hybrid radios in professional communication networks. In some cases, an organization may have an existing analogue infrastructure, but also needs to incorporate new digital functionalities. Instead of replacing the entire network, these organizations can opt for a hybrid solution, where radios can operate in both modes. This allows for a smooth transition to a fully digital network in the future, while maintaining operability in the present.
For example, in a public safety network, analog radios may still be used for basic voice communication, while new digital radios are integrated for more advanced tasks, such as sending critical data or streaming real-time video. This flexibility is key to maintaining operational efficiency while moving toward modernizing the communication infrastructure.
In summary, both analog and digital technology have their places in the radio communications arena.
Both analog and digital technologies have their place in modern communication. Understanding their differences helps you make informed decisions based on your specific needs and priorities. Whether you require basic voice communication or advanced data capabilities, Hytera offers a comprehensive range of solutions to keep you connected.





